Guide to Learning Blockchain Technology
Decentralization: The Cornerstone of Blockchain
At its core, blockchain technology thrives on decentralization. Unlike traditional systems where banks or governments hold centralized control, blockchain distributes record-keeping across a vast network of computers. This approach not only bolsters security but also makes the system resistant to censorship and less vulnerable to single points of failure. Decentralization ensures that no single entity can monopolize the data, fostering transparency and accountability throughout the entire ecosystem.
Cryptography: Ensuring Data Integrity and Security
The security of blockchain transactions hinges on advanced cryptographic techniques. Each block receives a unique digital fingerprint through hashing algorithms, which links it to the preceding block, forming an unbreakable chain. Public-key cryptography further enhances security by verifying participant identities and authorizing transactions, safeguarding the privacy and integrity of blockchain data.
Consensus Mechanisms: Reaching Agreement on the Ledger
For a blockchain network to function smoothly, consensus mechanisms are indispensable. These protocols determine how new blocks are validated and added to the chain. While Proof-of-Work (PoW) demands substantial computational resources, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) relies on participants' stakes. Selecting the right consensus mechanism is paramount as it directly impacts the network's efficiency and security.
Smart Contracts: Automating Agreements
Smart contracts revolutionize traditional agreements by embedding terms directly into executable code. These self-executing contracts eliminate intermediaries, reducing fraud risks and disputes. From supply chain management to decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts are transforming industries by enhancing efficiency and transparency.
Immutability: Ensuring Data Integrity and Trust
Once recorded on the blockchain, data becomes immutable—unalterable and permanent. This characteristic is crucial for applications requiring trustworthy records, such as financial transactions and digital identity verification. The permanence of blockchain records ensures data integrity, making it a reliable solution across various sectors.
Emerging research in nutritional neuroscience reveals how diet profoundly affects brain health and cognitive function. Essential nutrients like fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals play pivotal roles in maintaining mental acuity and preventing cognitive decline.
Different Blockchain Types and Their Use Cases
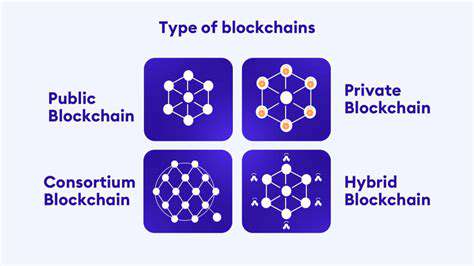
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on open-source, permissionless networks. Their transparency allows anyone to verify transactions independently, building trust through decentralization. However, this emphasis on security and decentralization can sometimes result in slower transaction speeds and scalability challenges.
Private Blockchains
Controlled by specific organizations, private blockchains offer tailored solutions for businesses. These networks typically achieve faster transactions and greater scalability compared to public blockchains. The trade-off, however, involves potential concerns about centralization and reduced transparency.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains strike a balance between public and private models. A select group of participants governs the network, enabling secure collaboration. This structure allows for optimized governance and security measures tailored to the consortium's specific needs.
Permissioned Blockchains
Permissioned blockchains provide flexible access control, making them ideal for businesses handling sensitive data. Granular permissions ensure that only authorized users can perform specific actions, enhancing security for specialized applications.
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains combine the best features of different blockchain types. This versatility enables customized solutions that address specific security, performance, and privacy requirements.
Sidechains
Sidechains operate alongside main blockchains, handling less critical transactions to improve scalability. By offloading certain processes, sidechains enhance the overall efficiency of the network.
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) Blockchains
DAG blockchains employ a non-linear structure for parallel processing. This innovative design significantly boosts transaction speed and scalability, though it may introduce complexities in security and consensus mechanisms.
Getting Started with Blockchain Development: Practical Steps
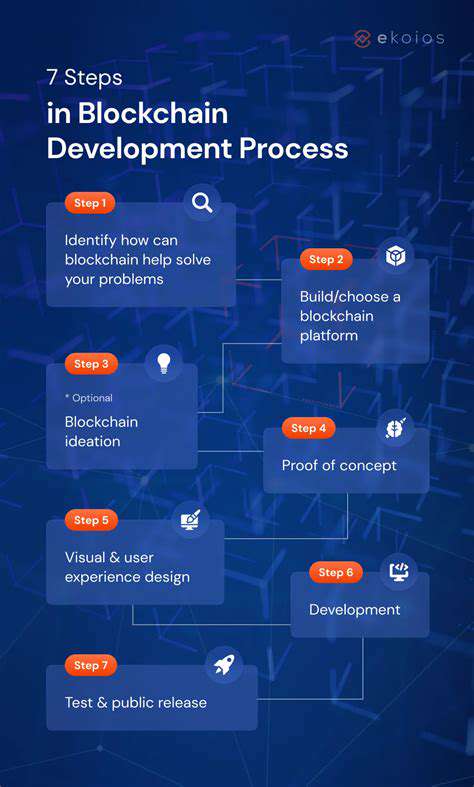
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain represents a paradigm shift in data management, offering a decentralized, immutable ledger. Grasping core principles like decentralization and transparency is essential for anyone entering this field.
Key Concepts in Blockchain
Decentralization ensures no single point of control, while immutability guarantees that recorded transactions remain tamper-proof. These features make blockchain ideal for applications requiring verifiable records.
Different Types of Blockchains
From public networks like Bitcoin to private enterprise solutions, choosing the right blockchain type depends on specific security and access needs.
Blockchain Applications
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is revolutionizing supply chains, digital identities, and voting systems. Its ability to enhance transparency and efficiency is driving adoption across industries.
Setting up a Blockchain Development Environment
Development environments vary by project requirements. Selecting appropriate tools and platforms is crucial for efficient blockchain development.
Learning Blockchain Programming Languages
Languages like Solidity, Go, and Python are fundamental for blockchain development. Solidity, in particular, is essential for Ethereum smart contract creation.
Exploring Blockchain Development Resources
Leveraging online tutorials and communities accelerates learning. Staying updated with blockchain advancements ensures developers remain competitive in this rapidly evolving field.
Read more about Guide to Learning Blockchain Technology
Hot Recommendations
- How to Stay Productive While Working Remotely
- Tips for Managing Conflict with Coworkers
- Entrance & Certification Exams (升学考试)
- How to Improve Your Storytelling Skills (Speaking)
- How to Find Profitable Side Hustles
- Tips for Preparing for the TOEFL iBT Home Edition
- Guide to Switching Careers from [Industry A] to [Industry B]
- How to Run an Effective Hybrid Meeting
- Tips for Marketing Your Side Hustle on Instagram






![Guide to Learning [Specific Photography Niche, e.g., Portrait Photography]](/static/images/32/2025-05/CompositionTechniquesforVisuallyAppealingPortraits.jpg)

![Best Tools for Team Collaboration [2025]](/static/images/32/2025-05/StreamliningProjectManagementforEfficiency.jpg)