Guide to Researching Different Industries
Defining Your Research Question
Every research project begins with a fundamental task: crafting a clear research question. This isn't just about identifying a topic - it's about pinpointing the exact knowledge gap you intend to fill. The difference between a vague inquiry and a sharply defined question often determines the success or failure of an entire project. When researchers fail to establish precise parameters, they risk wandering into unproductive territory that wastes time and resources.
Consider what truly fascinates you about your chosen subject. What specific mysteries or problems demand exploration? Memory techniques can help organize these thoughts systematically. The effort you invest in refining your question now will pay dividends throughout your research journey.
Identifying Relevant Concepts and Variables
With your research question established, the next crucial step involves breaking down its components. This analytical process requires identifying all key elements and understanding their interrelationships. This conceptual mapping serves as the foundation for your entire methodology, influencing everything from data collection approaches to analytical frameworks.
Ask yourself: What are the building blocks of my research question? How might they interact? This systematic approach prevents ambiguity and keeps your investigation focused and productive.
Establishing a Timeline and Resources
Successful researchers don't just dive in - they plan strategically. Creating a realistic timeline means more than setting deadlines; it requires understanding the rhythm of research work. Underestimating time requirements is one of the most common mistakes novice researchers make. Each phase - from literature review to final analysis - needs careful consideration.
Equally important is resource assessment. Beyond financial budgets, consider access to databases, equipment needs, and potential collaborators. Proper planning here prevents frustrating roadblocks later.
Literature Review and Background Research
The literature review isn't a formality - it's your intellectual foundation. Thorough engagement with existing scholarship accomplishes three vital goals: it prevents redundant work, reveals methodological approaches, and highlights genuine gaps in knowledge. This stage transforms your research from isolated effort to scholarly conversation.
Effective reviews go beyond summary; they analyze, compare, and synthesize diverse sources to build a comprehensive understanding of your field's landscape.
Methodology and Data Collection
Your methodology is the blueprint for your entire investigation. The choice between qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods isn't academic - it fundamentally shapes your findings' validity. This decision should flow naturally from your research question and literature review insights.
Consider not just what data to collect, but how to ensure its reliability. Will you use surveys, experiments, case studies, or archival research? Each approach carries distinct advantages and limitations that must align with your research objectives.
Analyzing Competitive Landscapes: Understanding the Players
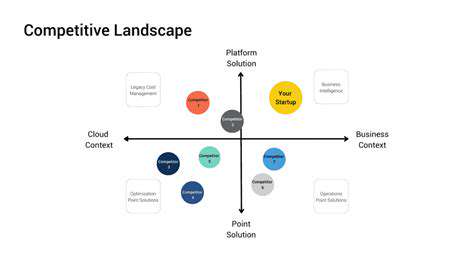
Understanding Market Dynamics
Market analysis begins with recognizing that industries are ecosystems in constant flux. The most successful businesses don't just react to changes - they anticipate them. This requires monitoring multiple indicators: technological disruptions, regulatory shifts, and evolving consumer expectations all interact in complex ways.
True market insight comes from connecting these dots to see patterns before they become obvious to competitors.
Identifying Key Competitors
Competitor identification demands a broad perspective. Beyond established rivals, watch for disruptive startups and adjacent industry players who might pivot into your space. Overlooking potential competitors is like preparing for yesterday's battle. Pay particular attention to companies with transferable technologies or unconventional business models.
Assessing Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Effective competitor assessment resembles strategic reconnaissance. Financial metrics tell only part of the story - cultural factors and organizational agility often determine long-term success. Examine not just what competitors do well, but where their blind spots might lie. Customer reviews, employee feedback, and supply chain vulnerabilities can reveal surprising weaknesses.
Analyzing Competitive Strategies
Strategy analysis requires decoding the thinking behind competitors' actions. Are they pursuing cost leadership, differentiation, or niche domination? Their pricing structures, marketing messages, and R&D investments form a pattern that reveals strategic intent. Look for inconsistencies between stated goals and actual resource allocation.
Evaluating Market Share and Growth
Market share analysis provides a snapshot, but growth rates indicate momentum. The most valuable insights come from comparing these metrics across time periods and geographic markets. A company losing share in stagnant markets might be more vulnerable than one gaining share in expanding ones.
Examining Distribution Channels and Networks
Distribution analysis often reveals hidden competitive advantages. Some companies thrive through exclusive retail partnerships, while others build unassailable direct-to-consumer networks. Innovative distribution can overcome product disadvantages, while outdated channels can undermine excellent products.
Forecasting Future Trends and Innovations
Trend forecasting combines data analysis with imaginative thinking. The most accurate forecasts balance quantitative projections with qualitative insights about human behavior. Watch for weak signals - small developments that might scale into major trends. Cross-industry innovations often provide the clearest windows into future disruptions.
Migraine disorders represent a complex neurological condition characterized by recurrent episodes of severe headache, often accompanied by sensory disturbances. Unlike typical tension headaches, migraines involve distinct physiological mechanisms that researchers continue to investigate.
Uncovering Market Trends and Forecasting Future Developments

Understanding the Dynamic Nature of Market Trends
Market trends resemble weather systems - visible on the surface but driven by deep, interconnected forces. The most successful analysts develop pattern recognition abilities that spot meaningful connections between seemingly unrelated developments. Interview techniques for market researchers emphasize this holistic perspective.
Effective trend analysis requires multiple data streams: sales figures, social sentiment, patent filings, and even geopolitical developments all contribute to accurate readings.
Identifying Key Drivers of Market Shifts
True market drivers often operate beneath surface-level explanations. What appears as changing consumer preferences might actually reflect deeper demographic shifts or technological enablement. The most powerful drivers frequently combine multiple factors - for instance, sustainability concerns merging with cost-saving technologies.
Forecasting Future Market Directions
Accurate forecasting requires balancing data-driven models with human intuition. The best forecasters use scenarios rather than predictions, preparing for multiple plausible futures. They understand that disruption often comes from unexpected directions, so they maintain wide peripheral vision while focusing on core indicators.
Analyzing Consumer Behavior and Preferences
Modern consumer analysis goes beyond demographics to examine psychographics and behavioral economics. The gap between stated preferences and actual behavior often reveals the most valuable insights. Neuromarketing techniques and ethnographic research provide windows into subconscious decision-making processes.
Evaluating Competitive Landscape Dynamics
Landscape analysis now requires monitoring both traditional competitors and potential disruptors from adjacent industries. The most significant competitive threats often emerge from unexpected directions. Ecosystem mapping helps identify these potential challengers before they become obvious threats.
Assessing Economic and Regulatory Influences
Economic and regulatory analysis has become increasingly nuanced. Smart analysts look beyond headline numbers to secondary effects and unintended consequences. For instance, environmental regulations might create unexpected opportunities for innovative materials or processes.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Market Trends
Technology's market impact extends far beyond obvious applications. The most transformative technologies often create indirect effects through enabling infrastructure or behavioral changes. Blockchain's potential extends beyond cryptocurrencies to supply chain transparency; AI's influence goes beyond automation to decision-making architectures.
Read more about Guide to Researching Different Industries
Hot Recommendations
- How to Stay Productive While Working Remotely
- Tips for Managing Conflict with Coworkers
- Entrance & Certification Exams (升学考试)
- How to Improve Your Storytelling Skills (Speaking)
- How to Find Profitable Side Hustles
- Tips for Preparing for the TOEFL iBT Home Edition
- Guide to Switching Careers from [Industry A] to [Industry B]
- How to Run an Effective Hybrid Meeting
- Tips for Marketing Your Side Hustle on Instagram





![Guide to Learning [Specific Photography Niche, e.g., Portrait Photography]](/static/images/32/2025-05/CompositionTechniquesforVisuallyAppealingPortraits.jpg)
![Best Tools for Team Collaboration [2025]](/static/images/32/2025-05/StreamliningProjectManagementforEfficiency.jpg)

