Tips for Reviewing Exam Material Effectively

Active Recall and Memory Consolidation
Active recall transforms learning by requiring you to pull information from memory rather than just reviewing it passively. Unlike passive reading, this method makes your brain work harder, sparking deeper cognitive engagement and fortifying memory links. When you actively retrieve facts, you're not just learning - you're building mental muscle that lasts. This retrieval process reinforces neural connections, making memories more accessible and durable over time.
Every time you struggle to recall something, you're actually strengthening the brain pathways for that knowledge. This isn't about simple recognition - it's about actively reconstructing knowledge, which is essential for creating lasting memories.
Retrieval Practice and Long-Term Retention
Retrieval practice, the cornerstone of active recall, means attempting to remember without checking your notes. Research consistently shows this outperforms traditional methods like highlighting or rereading. The magic happens in your neurons - each successful retrieval makes those pathways stronger and more reliable. This creates memories that resist fading, staying available when you need them most.
Think of retrieval practice as mental weightlifting - each attempt builds a more resilient memory structure. This robust framework lets you access and use information flexibly across different situations, leading to truly effective learning.
Implementing Active Recall Strategies
You can start using active recall today with simple tools like flashcards or self-quizzing. The key is forcing yourself to generate answers rather than just review them. Try explaining concepts aloud as if teaching someone else - this Feynman technique reveals gaps in understanding. Practice tests work wonders too, especially when you create them yourself.
The golden rule? Make your brain do the work of retrieval. Passive review feels easier but delivers far weaker results. Active engagement is what builds real, lasting knowledge.
Benefits of Active Recall Beyond Learning
This technique isn't just for students - it's a life skill. Whether memorizing a speech, learning a language, or remembering important dates, active recall helps. It's like upgrading your brain's filing system - making important memories easier to find when life demands them. Professionals use it to master complex procedures, technical details, and client information.
In any field where remembering matters, active recall gives you an edge - helping you work smarter, not harder. It's not just about knowing more, but about making your knowledge reliably available.
Spaced Repetition for Long-Term Retention
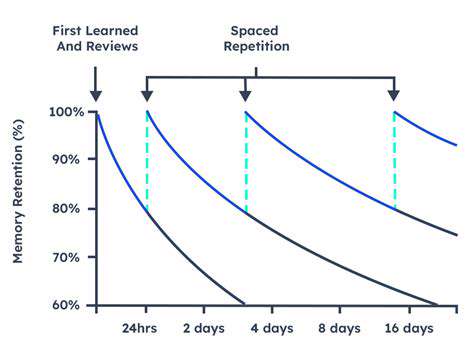
Spaced Repetition: The Core Concept
Spaced repetition is a smart learning strategy that times reviews based on when you're about to forget. Instead of marathon study sessions, you revisit material at scientifically optimized intervals. This method works with your brain's natural forgetting curve, targeting reviews exactly when they're most needed. It's efficient because you spend time only on what's slipping away, not what you've already mastered.
This approach recognizes that memory isn't built in one go - it's layered through repeated, timed exposures. Each review session cements the knowledge more firmly in your mind.
The Power of Increasing Intervals
The genius of spaced repetition lies in its adaptability. Remember something easily? The system waits longer before asking again. Struggle with it? You'll see it sooner. This personalized pacing creates the most efficient learning rhythm possible for your unique memory. It's like having a personal trainer for your brain, constantly adjusting the workout to maximize results.
This dynamic adjustment means you're always working at the edge of your memory capacity - the sweet spot where learning happens most effectively.
Applications Across Disciplines
From medical students memorizing anatomy to language learners acquiring vocabulary, spaced repetition delivers results. Its flexibility makes it ideal for any subject requiring long-term retention. Particularly in fields like medicine or law where knowledge builds cumulatively, this technique prevents the all-too-common learn and forget cycle. Even programmers use it to remember complex syntax and algorithms.
The method adapts to any content, making it a universal tool for knowledge retention. Whether you're learning piano chords or historical dates, spacing out your practice yields better results.
The Role of Technology in Spaced Repetition
Modern apps have transformed spaced repetition from theory to daily practice. These tools handle all the scheduling complexity, letting you focus on learning. With algorithms tracking your performance and optimizing review timing, you get personalized memory training without the mental overhead. Many apps even sync across devices, making practice possible anytime, anywhere.
Building a Personalized Learning Strategy
While technology helps, success comes from tailoring the system to your needs. Pay attention to which material needs more focus and adjust accordingly. The most effective learners don't just follow the system - they make it work for their specific goals and challenges. Track what works and refine your approach over time.
Remember that spaced repetition isn't magic - it's a tool. Used thoughtfully alongside other techniques, it can dramatically boost your learning efficiency.
Maximizing Retention Through Active Recall
Combine spaced repetition with active recall for explosive results. Instead of just reviewing notes, test yourself at each interval. This powerful combination forces deep engagement with material, creating knowledge that sticks. It's the difference between recognizing information and being able to produce it when needed.
When you actively retrieve information at optimally spaced intervals, you're not just learning - you're building expertise that lasts.
Utilizing Effective Note-Taking Strategies

Effective Note-Taking Strategies for Enhanced Learning
Smart note-taking is more than transcription - it's active engagement with information. The best notes don't capture every word, but distill key concepts into a personalized format that aids later recall. Your notes should work for you, not just record what was said. A good system reduces exam stress by making review sessions more productive.
Experiment with different methods until you find your perfect match. Some learners thrive with visual mind maps, others prefer structured outlines. Incorporate symbols, diagrams, and color coding to make connections visible. The act of organizing information as you take notes actually begins the learning process.
Optimizing Note-Taking Techniques for Different Learning Environments
In lectures, focus on capturing the professor's main arguments and evidence, not every word. Develop your own shorthand to keep pace while maintaining comprehension. Leave space to add connections and questions later. This selective approach lets you engage with the material rather than just transcribe it.
When reading complex texts, summarize sections in your margin notes. Try restating key ideas in your own words - this simple act dramatically improves retention. By processing information through your own linguistic filters, you make it truly yours. Highlight judiciously, focusing on concepts rather than whole paragraphs.
Group discussions demand a different approach. Capture multiple perspectives, noting areas of agreement and contention. Record action items clearly. This develops your ability to synthesize diverse viewpoints - a crucial professional skill.
Adapting your note-taking style to different contexts makes you a more versatile learner. Whether in a lecture hall, reading room, or team meeting, your notes should serve your specific needs in that moment.
Read more about Tips for Reviewing Exam Material Effectively
Hot Recommendations
- How to Stay Productive While Working Remotely
- Tips for Managing Conflict with Coworkers
- Entrance & Certification Exams (升学考试)
- How to Improve Your Storytelling Skills (Speaking)
- How to Find Profitable Side Hustles
- Tips for Preparing for the TOEFL iBT Home Edition
- Guide to Switching Careers from [Industry A] to [Industry B]
- How to Run an Effective Hybrid Meeting
- Tips for Marketing Your Side Hustle on Instagram
![Best Online Writing Courses [Fiction & Non Fiction]](/static/images/32/2025-04/StayingMotivatedandConsistent3ASustainingYourWritingJourney.jpg)