How to Improve Your Handwriting (for Note Taking)
Posture and Hand Position: Ergonomics for Effective Note-Taking
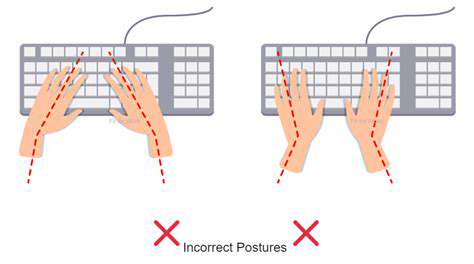
Posture for Optimal Ergonomics
Maintaining proper posture is crucial for preventing musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) associated with prolonged computer use. Keeping your back straight and avoiding slouching or hunching over your keyboard is essential. This alignment helps distribute weight evenly across your spine, reducing strain on your neck, shoulders, and back. Proper posture also enhances blood flow and breathing, contributing to overall well-being.
Make sure your feet are flat on the floor, or use a footrest if needed. This stable base supports proper posture and prevents lower back strain. Aim for a neutral spine position, avoiding excessive arching or rounding of the back.
Hand Position During Typing
Maintaining a neutral wrist position is critical to avoiding repetitive strain injuries (RSIs). Avoid bending your wrists excessively when typing, as this stresses tendons and ligaments. Keep your wrists straight and aligned with your forearms.
Position your hands comfortably on the keyboard, avoiding unnecessary reaching or stretching. Adjust your keyboard height to minimize wrist bending and reduce tension in your hands and arms.
Keyboard Placement and Height
Place the keyboard directly in front of you for natural arm and hand movement. Avoid positioning it too far or too close, as this affects posture. An ideal height keeps your forearms parallel to the floor while typing, reducing strain on wrists and elbows.
Mouse Placement and Use
Proper mouse placement is essential for preventing hand and wrist strain. Keep your mouse near the keyboard to avoid stretching or twisting your wrists. This minimizes strain on your wrist and forearm, lowering the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
Use smooth mouse movements and avoid abrupt actions. This reduces stress on tendons and ligaments, preventing strain injuries over time. A well-placed mouse also enhances typing efficiency.
Ergonomic Accessories
Ergonomic accessories can significantly improve your workspace. An adjustable chair lets you customize height and support to fit your needs, maintaining proper posture and reducing long-term discomfort.
Consider a wrist rest for additional cushioning and support while typing. Dedicated ergonomic keyboards and mice can greatly minimize strain on your wrists, hands, and forearms.
Practicing Handwriting Techniques: Mastering the Art of the Stroke
Understanding the Fundamentals of Handwriting Strokes
Effective handwriting relies on mastering fundamental strokes. These basic building blocks form letters, numbers, and symbols. By practicing controlled movements, consistent pressure, and proper angles, you’ll develop a fluid and legible style. Smoothly connecting strokes is key to polished handwriting.
Different strokes require varying pressure and speed. Mastering these nuances improves the appearance and clarity of your writing.
Practicing Letter Formation
Focus on precise letter formation, paying attention to starting points, curves, and ending strokes. Handwriting guides or templates can help ensure accuracy.
Practice uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols to enhance overall skill.
Developing Consistent Pressure and Speed
Maintain even pressure and controlled speed for legible handwriting. Exercises promoting consistency result in uniform strokes, avoiding uneven or heavy/light writing.
Mastering the Angle and Position of Your Hand
Hand angle and position impact handwriting legibility. Experiment with different angles to find what works best and minimizes strain.
Using Handwriting Guides and Templates
Guides and templates provide a visual framework for practicing correct letter formation. They help develop a consistent and readable style.
Explore digital or physical guides to suit your learning preferences.
Incorporating Regular Practice into Your Routine
Daily practice builds muscle memory and improves handwriting. Short, focused sessions yield gradual improvements over time.
Consistency is essential for mastering handwriting skills.
The Role of Handwriting in Communication and Expression
Handwriting enhances communication and reflects personality. A legible style makes writing more engaging, while artistic strokes allow for creative expression.
Identifying potential hazards is crucial for safety. Assess the environment, activities, and individuals involved. Proactive observation helps anticipate and mitigate risks. Hazards range from slips to equipment malfunctions or severe weather. Understanding each hazard’s nature and likelihood is the first step in risk management.

Regular Practice and Feedback: Consistency is Key
Consistent Practice: The Foundation of Improvement
Regular practice improves handwriting. Daily sessions build muscle memory and hand-eye coordination, much like learning an instrument. Start with basic letter formations and progress to complex compositions for natural rhythm and fluidity.
Understanding Your Current Handwriting Style
Analyze your handwriting for slants, pressure, and spacing. Identify inconsistencies in letter size or shape to target areas for improvement.
Utilizing Handwriting Guides and Resources
Guides and online resources offer structured exercises and demonstrations. They provide clarity on proper techniques and styles.
The Importance of Proper Posture and Hand Positioning
Good posture prevents strain and promotes fluid movement. A relaxed hand position ensures consistent, clean letter formation.
Seeking Feedback from Others
Constructive feedback from teachers or peers highlights unnoticed flaws, guiding targeted improvements.
Effective Exercises for Handwriting Practice
Practice tracing letters, writing sentences, and experimenting with pens and paper textures to refine your style.
The Role of Patience and Persistence
Handwriting improvement requires time and dedication. Celebrate small progress and stay persistent to achieve your goals.
Read more about How to Improve Your Handwriting (for Note Taking)
Hot Recommendations
- How to Stay Productive While Working Remotely
- Tips for Managing Conflict with Coworkers
- Entrance & Certification Exams (升学考试)
- How to Improve Your Storytelling Skills (Speaking)
- How to Find Profitable Side Hustles
- Tips for Preparing for the TOEFL iBT Home Edition
- Guide to Switching Careers from [Industry A] to [Industry B]
- How to Run an Effective Hybrid Meeting
- Tips for Marketing Your Side Hustle on Instagram