How to Use Mnemonics for Remembering Information
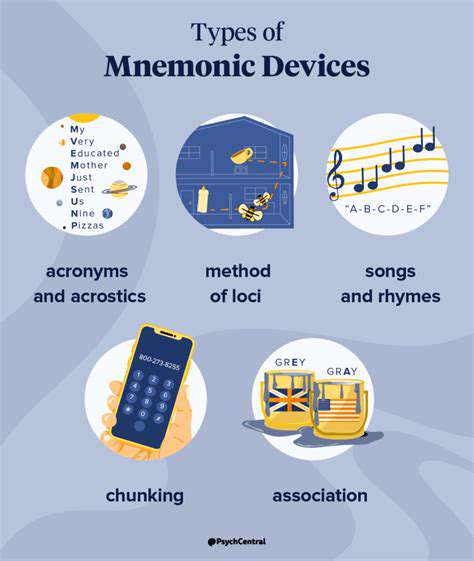
What are Mnemonics?
Mnemonics function as cognitive tools, structured approaches crafted to enhance information retention. Rather than relying on repetition, they forge connections between new data and existing knowledge through creative associations or mental imagery. This approach fortifies neural pathways, streamlining recall.
At their core, these techniques serve as intellectual bridges, transforming passive memorization into an active, engaging mental exercise. Grasping their fundamental mechanisms unlocks their potential for both academic pursuits and everyday challenges.
Types of Mnemonics
The landscape of memory techniques offers diverse options, each with unique advantages. Common varieties include word-based systems (acronyms and acrostics), visual linking methods, and spatial strategies like the memory palace. Acronyms compress information into memorable abbreviations, while acrostics weave first letters into meaningful phrases.
Recognizing these distinct approaches enables users to select the most fitting technique for specific information types or learning objectives.
The Power of Association
Association forms the bedrock of effective memorization. When we anchor unfamiliar concepts to well-known references or striking mental pictures, we forge durable cognitive connections. This bridging of known and unknown information facilitates effortless retrieval.
This associative principle represents the golden thread running through all successful memory enhancement methods.
Visual Imagery and Memory
Mental visualization stands as one of mnemonics' most potent weapons. Transforming abstract data into colorful, dynamic mental scenes dramatically improves recall accuracy. Picture a flamboyant scenario where concepts interact in unexpected ways - the more peculiar and detailed, the more indelible the memory.
Converting intangible information into vivid sensory experiences creates lasting cognitive imprints.
The Method of Loci
This ancient technique, often called the memory palace, employs spatial memory as an organizational framework. Users mentally place informational items along familiar routes or within known environments, creating geographic memory cues. Each location serves as a mental file folder for associated data.
Regular mental navigation of these memory landscapes strengthens recall pathways through repetition and spatial reinforcement.
Acronyms and Acrostics
These linguistic tools offer straightforward yet powerful memorization solutions. Acronyms distill complex information into compact word forms, while acrostics create memorable sentences from initial letters. Both excel at organizing sequential or categorical information.
Their simplicity belies their effectiveness in creating mental handles for grasping complex information clusters.
Practical Applications and Benefits
Memory techniques find utility across countless domains, from academic study to professional skill retention. Strategic application of these methods can transform information overload into manageable, retrievable knowledge structures.
Developing proficiency in these cognitive tools creates measurable advantages in learning efficiency and knowledge retention across all life domains.
The Method of Loci: Mapping Information to Familiar Spaces
Understanding the Method of Loci
The memory palace technique represents a sophisticated cognitive mapping strategy that harnesses our innate spatial awareness. By assigning information fragments to specific locations within mentally reconstructed environments, we create a geographic memory index. This mental architecture transforms abstract data into tangible spatial relationships, mirroring how our ancestors navigated physical landscapes.
Visualize mentally strolling through your childhood home. Assign distinct pieces of information - historical dates, foreign vocabulary, or mathematical formulas - to particular rooms or objects. The key lies in crafting unusual, emotionally charged mental images at each location. A giant calculator dancing on the kitchen table or Shakespeare reciting sonnets in your bedroom creates indelible memory markers. This spatial-anchored visualization capitalizes on our evolutionary predisposition for remembering locations and routes.
Creating Your Memory Palace
Effective memory palaces require carefully selected, well-known environments rich in sensory details. Ideal candidates include childhood homes, daily commutes, or frequently visited buildings. The environment should be mentally reconstructible with crystal clarity - every piece of furniture, wall color, and architectural feature serving as potential memory waypoints.
After selecting your location, conduct a mental walkthrough, noting distinctive features where information will reside. For remembering a speech, you might visualize your opening statistic as a glowing billboard on your front porch, with subsequent points appearing as animated objects in each room. These mental placeholders should engage multiple senses - imagine not just seeing but hearing and touching these imagined objects.
Remembering Information with the Method of Loci
Memory retrieval becomes an exercise in mental navigation. Begin your recall by standing at your palace's entrance, then systematically progress through each location. The vivid mental markers you've planted will trigger associated information in sequence. Encountering a talking refrigerator in your mental kitchen might cue your next business presentation point, while a floating textbook in the hallway recalls key statistical data.
Mastery develops through consistent practice. Initially, spend time mentally decorating your palace before important memorization tasks. With repetition, this process becomes increasingly fluid, eventually allowing spontaneous creation of new memory palaces for different information sets. The technique's true power emerges when users can construct and navigate multiple specialized memory landscapes for various knowledge domains.
Read more about How to Use Mnemonics for Remembering Information
Hot Recommendations
- How to Stay Productive While Working Remotely
- Tips for Managing Conflict with Coworkers
- Entrance & Certification Exams (升学考试)
- How to Improve Your Storytelling Skills (Speaking)
- How to Find Profitable Side Hustles
- Tips for Preparing for the TOEFL iBT Home Edition
- Guide to Switching Careers from [Industry A] to [Industry B]
- How to Run an Effective Hybrid Meeting
- Tips for Marketing Your Side Hustle on Instagram
![Best Prep Courses for the GMAT [2025]](/static/images/32/2025-05/BeyondtheClassroom3AAdditionalResourcesforGMATSuccess.jpg)




![Best Resume Action Verbs for [Specific Industry]](/static/images/32/2025-05/ElevatingYourCommunication26PresentationSkills.jpg)